Notary publics are tasked with proving the authentication and certification of legal documents and attached signatures. The Notary profession, its processes and practices have seen rapid changes with the rise of globalization and the more recent requirement for public services to be available digitally, which has also resulted in new regulations to protect these fundamental legal processes from digital security risks.
Due to these developments, the greatest impact to the notary public profession has been the rise of digital notarization, where documents can be signed and notarized electronically. The benefits of digital notarization are far reaching for the legal sector as well as the individuals and businesses that they serve. Digital notarization allows clients and notaries to bypass in-person meetings, providing greater accessibility to notarial services for those to whom travelling may not be an option, as well as allowing for faster, more efficient processing of notarial and legal documents.
However, the digitization of legal and notarial documents and procedures can leave it exposed to security vulnerabilities without the right protection, rendering the whole notarial process redundant. The notarial profession must adapt quickly to these new challenges in order to ensure the security of critical legal documentation and protect the interests of the public, whom they serve, embracing digital security practices with an emphasis on data protection and regulatory compliance.
- Remote Online Notarization (RON) vs Traditional Notarization
- Legal Frameworks for Remote Online Notarization
- The Role of Digital Signatures and Seals for Remote Online Notarization Services
- Practical Applications of Digital Signatures and Seals in the Notarial Profession
- The Importance of Trust in Remote Online Notarization
Remote Online Notarization (RON) vs Traditional Notarization
Notarization is the process of having a notary public verify the authenticity of legal documentation and the identity of the signing parties. This process generally remains the same for both traditional notarization and digital notarization, but with a few key differences in how it is performed.
When a document is notarized digitally, it is important to be aware that there are two types of digital notarization. ‘Electronic notarization’ is the general term for notarial acts that are performed digitally, including in-person notarial acts, where the documentation is signed on a device such as a tablet or laptop. Alternatively, documentation can be signed and notarized online. This service is known as Remote Online Notarization (RON).
Traditionally, participants are required to appear before a commissioned notary public when fulfilling in notarial acts, providing proof of identity before the documentation is signed and notarized. If this is performed through an RON service, this can be achieved through a live video and audio call while completing the document digitally.
Due to their benefits of greater accessibility, RON services are becoming more mainstream and widely available. Remote Online Notarization offers clients:
- Greater Speed and Efficiency: As online meetings render travelling and the processing of physical paperwork unnecessary, notarial acts are processed far more quickly allowing individuals and organizations to move on with the next steps of legal proceedings much more quickly, at greater convenience for the client and notary.
- More Easily Available Cross-border Services: In the wake of globalization, the remote nature of RON services also allows notaries to work more easily with international citizens, global embassies and foreign offices and legal service providers. This is also having a knock-on impact on the number of notaries who are acquiring skills in navigating a more diverse range of international legal systems.
- Sustainability: Paperless offices are becoming the norm across all industries following national lockdown mandates, and the legal and notary sectors are no exception. RON services require little to no paperwork meaning the adoption of greater sustainability practices in notarial offices.
- Auditable Trail: As well as paperless offices, RON practices have also resulted in an easier to follow auditable trail of documentation, as contracts and notarial paperwork can be stored using cloud-based platforms rather than filed in a cabinet, granting access to anyone who needs it with authorization.
Legal Frameworks for Remote Online Notarization
e-Notarization is becoming a legally accepted process globally and while state and national governments everywhere will legislate their own definition of accepted RON requirements, they generally tend to follow the same core guidelines; for example, the notary must be able to verify the client identity via a video and voice call. There are also some notarial acts which can only be performed in person such as the notarization of birth and death certificates, but generally most notarial acts can be performed remotely if requested and if they are provisioned for in the law.
In the US, RON and e-Notarial services are held to a number of regulatory requirements including the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA), the ESIGN Act and the National Association of Secretaries of State’s (NASS) E-Notarization Standards. At present, 47 American States and the District of Columbia legally accept e-Notarization and RON services, although standards vary between them and many are still developing their frameworks.
- UETA, 1999: Developed to remove barriers to electronic signing processes, this states that electronic signatures, including any symbol, sound or other process, can be legally used in place of traditional signatures for notarial acts, provided that all parties consent and have access to and awareness of the software and hardware used for electronic signing of the document and can retain access.
- E-SIGN Act, 2000: This was developed to support and work with the requirements of UETA, there is significant overlap between the two regulations. This allows for document signers and notaries to submit any symbol, sound or other process as their legal signature so long as it is “attached” or “logically associated” with the document and other required notarial information such as the notarial certificate and seal information. While the UETA guidelines are optional for each state, the ESIGN act operates at federal level and means that one state cannot reject the legal authenticity of an electronic signature, reducing restrictions for organizations operating at an interstate level.
- NASS E-Notarization Standards, 2006: This expands on both UETA and the E-SIGN Act, with a more specific definition of a notary’s signature. In addition to the requirements defined in UETA and ESIGN, these standards require that the signature is unique to the notary, can be independently authenticated, controlled solely by the notary themself, that it is linked to the document in a way that subsequent alterations would be detectable. These standards are important because they cannot be achieved solely with a Simple Electronic Signature.
In the UK and the EU notaries are subject to GDPR which requires them to ensure the security of client data, including any documentation with their personal information or that they have signed.
Remote Online Notarization processes also fall in line with eIDAS in both the UK and EU. While eIDAS does not stipulate that notarization is a requirement of compliance, it does provide a framework for the legal requirements around the use of digital signatures. This applies to a broad range of use cases for digital signatures which can include RON services such as cross-border services, and the standardization of requirements for accepted signature types across the EU and UK.
eIDAS, as well as defining different types of electronic signatures, including Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) for their high level of security and legal assurance, it also states that electronic signatures shall not be denied legal admissibility as evidence solely based on the grounds that they are electronic. It also specifies standards for the use of Advanced Electronic Signatures and Seals (AES) to ensure cross-border interoperability. While this does not specifically discuss their uses in notarial processes, this is important for enabling RON services spanning multiple jurisdictions.
Overall, notaries must have a diverse understanding of international legal frameworks and signature types if they are to provide cross-border services, and RON services must provide a strong level of trust and assurance to ensure that signatures and seals are legally recognized regionally.
Discover more information on regional guidelines for digital signatures and seals
The Role of Digital Signatures and Seals for Remote Online Notarization Services
Digital signatures and seals ensure security and trust, the latter being fundamental to the notarial process. Digital signatures are used in the Remote Online Notarization process for a number of reasons:
- Identity Verification: Digital signatures require with a Certificate Authority (CA) to verify the signer’s identity. The CA issues digital certificates that verify the identity of individuals or organizations, ensuring that the signer is who they claim to be.
- Security and Integrity: Digital signatures ensures that a document has not been tampered with after signing. Through encryption they create a unique digital fingerprint of the document, which can be verified by anyone with access to the signer's public key.
- Legal Recognition: Digital signatures are legally recognized in many jurisdictions worldwide and can therefore be used in the notarization process in compliance with regional requirements.
Types of Digital Signatures for Remote Online Notarization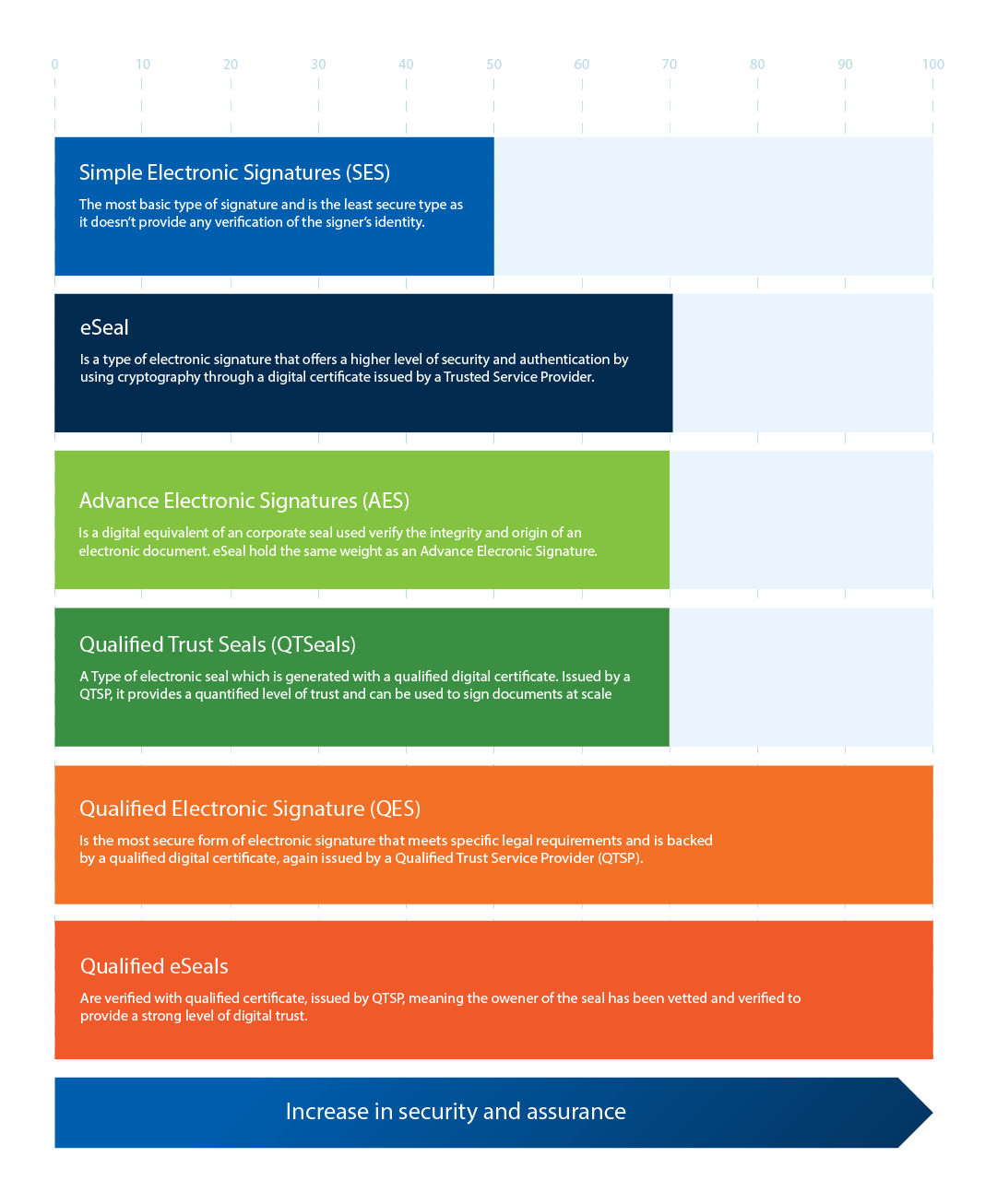
Discover digital signatures and seal solutions and secure notarized documents
Practical Applications of Digital Signatures and Seals in the Notarial Profession
- Real Estate: Digital Signatures for RON services means that property transactions can be streamlined through signing contracts remotely whilst ensuring a high level of authenticity and assurance.
- Finance and Insurance: Secure signing of loan agreements, bank statements and investment agreements provide assurance and efficiency for financial institutions such as banks and credit unions as well as in-house organization finance teams. Digital signatures and seals also expedite claims processing, ensuring that documentation has not been tampered with.
- HR and Employment: Through secure Remote Online Notarization using digital signing services, organizations can facilitate remote onboarding of new employees as well as other employee documentation including title changes and HR processes.
- Other Notarial Acts: In the legal sector, document signing solutions can ensure the authenticity and security of critical legal documentation, including affidavits, powers of attorney, wills, marriage licenses and visa applications. In the case of overseas clients and visa and other travel documentation, Remote Online Notarization is a much more accessible option, as well as for those who may not be able to travel due to personal circumstances. In this case, the use of digital signatures and seals is imperative to ensure the security and authenticity of notarized documentation.
The Importance of Trust in Remote Online Notarization
For notary publics, trust is paramount. Their role is to ensure the authenticity of legal documentation so that it cannot be disputed. In an increasingly digitized landscape and the context of evolving technological developments, this can present challenges to Remote Online Notarization. If a notarized document is found to be insufficiently secured or to have been tampered with, this could result in a loss of trust as well as legal disputes, invalidation of contracts and paperwork and financial losses. Additionally, should a piece of documentation become compromised, this could leave client’s personal or business information exposed, and result in a critical data leak. Not to mention regulatory fines and reputational damage that would follow.
It is imperative to work with a publicly trusted Certificate Authority for secure, certificate-based signatures and seals. Not only can they help provide greater efficiency and accessibility throughout the notarial process, they ensure security and authenticity to critical documentation, and help provide non-repudiation, working to uphold the trust that notarial professionals strive to guarantee their clients.
GlobalSign is a leading provider of digital signing solutions and has been a publicly trusted Certificate Authority for over 25 years. GlobalSign’s PKI-based document signing solutions are in line with the Adobe Approved Trust List, designed to bring you a high-level of security and assurance, while simplifying and streamlining document workflows.
Ensure trust in critical legal documentation with GlobalSign document signing solutions
Editor’s Note: This blog was originally published in April 2020 but has since been reviewed to ensure that the content is in line with industry standards, regulations and insights.







