The terms electronic signatures and digital signatures are often used interchangeably, yet there are some key differences between them. While electronic signatures encompass a broad range of methods for digitally signing documents, digital signatures specifically utilize advanced cryptographic techniques to add an extra layer of security and authentication to the signed documents.
Both types of signatures have their own advantages. Join us as we break them down and explore everything you need to know about electronic and digital signatures.
- What is an Electronic Signature?
- What is a Digital Signature?
- What's the Difference Between Electronic Signatures and Digital Signatures?
- Benefits of Digital Signatures
- What Industries and Use Cases Are There for Digital Signatures?
- How to Choose the Right Document Signing Solution
- Best Practices for Implementing Digital Signatures
- Future Trends in Digital Signing
- To Summarize: Digital Signatures are More Secure
What is an Electronic Signature?
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is a digital representation of an individual's intent to sign a document or agreement. These signatures can take various forms, including scanned images of handwritten signatures, typed names, or even recorded voices.
More loosely, e-signatures are used to refer to any signature that's applied electronically as opposed to on a physical piece of paper. An electronic signature does not confirm the content within a document, or provide security and assurance. Additionally, not all electronic signatures’ assurance levels are the same in the eyes of the law. Highly regulated sectors, such as finance or accounting, HR, legal, and healthcare should consider a more secure option to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
What is a Digital Signature?
A digital signature is a type of electronic signature that uses cryptographic technology to create a digital certificate, to provide proof of an identity. By creating a unique digital fingerprint, digital signatures provide the highest level of security assurance by verifying the signer’s identity. This is done through a trusted third party, known as a Certificate Authority (CA).
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are digital signatures, as they are backed with cryptography and provide security assurance of varying levels.
Digital signatures assure that:
- The document is authentic and comes from a verified source.
- Identities have been verified by a publicly trusted organization (the CA).
- The document has not been tampered with since being digitally signed as the signature would be displayed as invalid if changes were made.
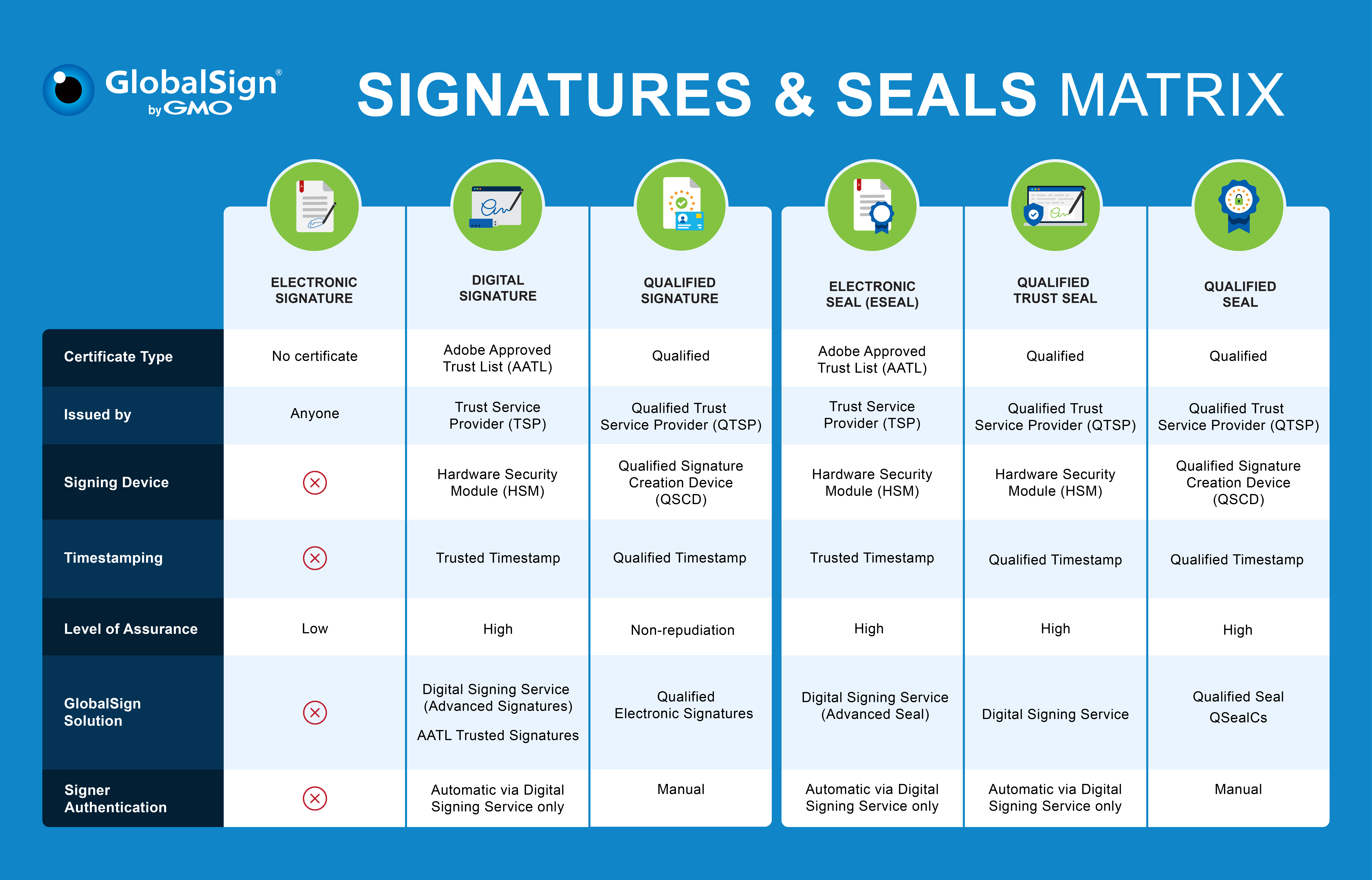
What are the Different Types of Digital Signatures?
There are five types of signatures:
- Simple Electronic Signatures (SES) – the most basic type of signature and is the least secure type as it doesn’t provide any verification of the signer’s identity.
- Electronic Seal (eSeal) – is a digital equivalent of a corporate seal used to verify the integrity and origin of an electronic document. eSeals hold the same weight as an Advanced Electronic Signature.
- Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) – is a type of electronic signature that offers a higher level of security and authentication by using cryptography through a digital certificate issued by a Trust Service Provider.
- Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) – is the most secure form of electronic signature that meets specific legal requirements and is backed by a qualified digital certificate, again issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP).
- Qualified eSeals – are verified with a qualified certificate, issued by a QTSP, meaning the owner of the seal has been vetted and verified to provide a strong level of digital trust.
- Qualified Trust Seals (QTSeals) - A Type of electronic seal which is generated with a qualified digital certificate. Issued by a QTSP, it provides a quantified level of trust and can be used to sign documents at scale.
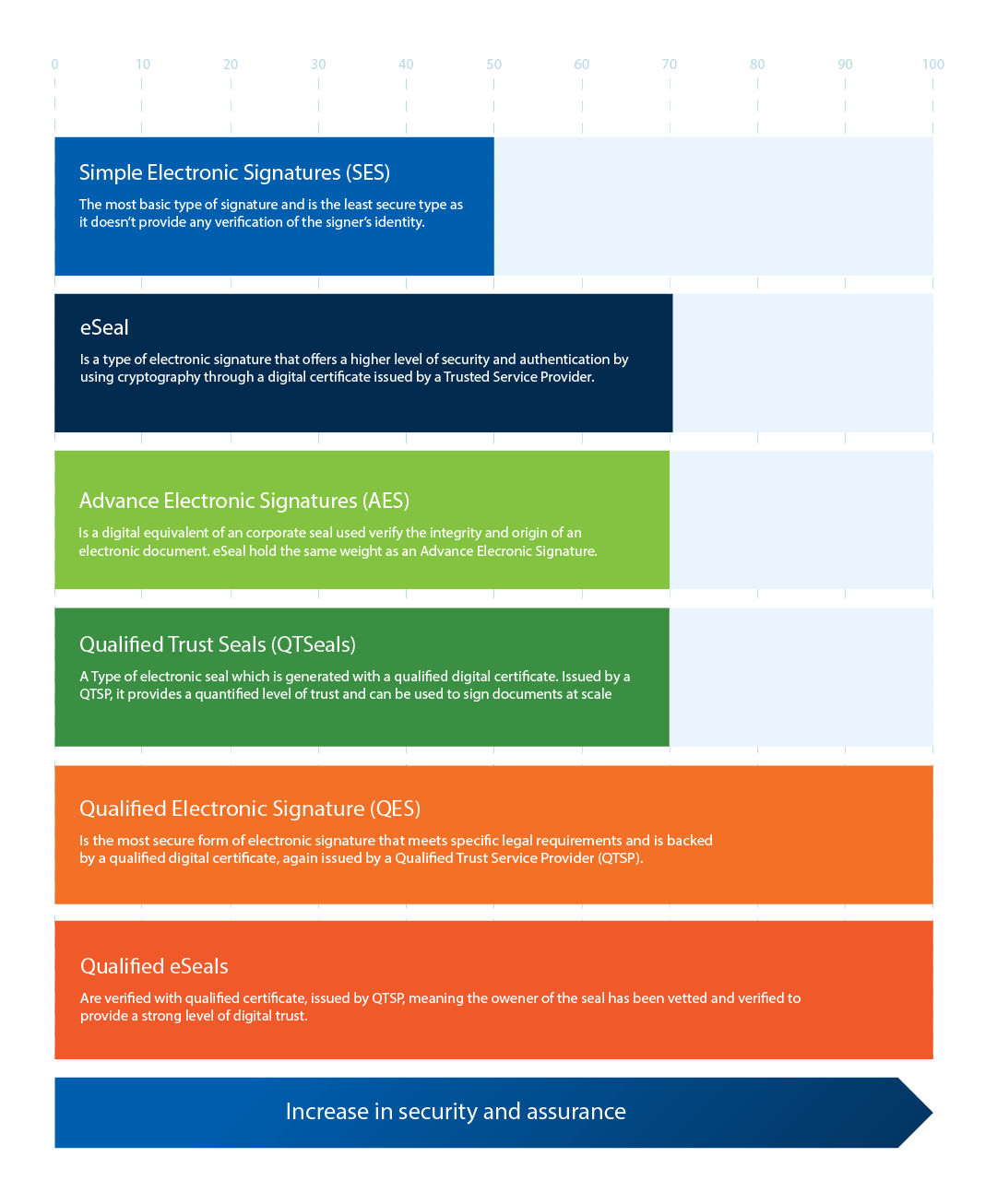
It’s important to understand the different types of electronic signatures available, and ultimately which type provides the best level of security required for an individual and/or business.
Are Digital Signatures Legal?
Yes, digital signatures are recognized as legally binding. But it is important to note that there are different types of signatures which hold a different weight. For example, a Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) cannot be disputed or be denied admissibility as evidence as it is uniquely tied with the signer’s identity.
Various laws and regulations, such as the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act in the United States and the eIDAS Regulation in the European Union, provide a legal framework for the use and acceptance of digital signatures. It is important to familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations in your jurisdiction to ensure compliance and legal validity.
Check your regional legal guidelines for digital signatures
What's the Difference Between Electronic Signatures and Digital Signatures?
There are number of differences between electronic signatures and digital signatures, from the technology and infrastructure used to deploy and the level of security and authentication, to legal frameworks and compliance requirements across and, use cases and industry adoption.

Electronic signatures encompass a wide range of methods for signing documents, while digital signatures also offer advanced security and authentication measures using cryptographic technology.
Below is a more detailed breakdown of the main differences:
- Technology and Infrastructure: Electronic signatures can be applied with a range of methods, including scanned images of handwritten signatures, typed names, or recorded voices. Digital signatures, on the other hand, create a unique digital fingerprint of the document using cryptographic technology, providing enhanced security and integrity.
- Level of Security and Authentication: Digital signatures provide a higher level of security compared to electronic signatures. Electronic signatures do not provide security, assurance or confirmation of the content within a document.
- Legal Frameworks and Compliance Requirements: Digital signatures require the use of a certificate issued by a Qualified Trust Services Provider (QTSP) to establish the identity of the signer. A QTSP provides the verification of the signer’s identity and must comply within the regulations, such as eIDAS. On the other hand, electronic signatures may not meet the legal requirements and acceptance can vary.
- Use Cases and Industry Adoption: Documents which have been signed electronically in the simplest form, have increased over the years and across several industries. Digital signatures however, due to their enhanced security and legal validity, are typically preferred in situations where there is a need for higher levels of integrity and non-repudiation, such as in financial transactions, legal documents, or sensitive agreements.
Benefits of Digital Signatures
There are number of benefits of using digital signatures, including:
- Cost and Time-saving Advantages: Digital signatures streamline the signing process as documents can be signed and shared instantly, saving time and reducing delays in transactions.
- Enhanced Security: By using digital signatures and the cryptographic elements, a signed document can retain its integrity and authenticity and provide a high level of security, and reduces the risk of fraud and tampering.
- Improved User Experience: Digital signatures can enhance the experience by offering the flexibility to sign documents from anywhere, at any time, using any device with an internet connection.
- Cost Savings and Environmental Sustainability: The need for printing, paper, ink and postage is eliminated saving on cost associated with physical documentation whilst also contributing to environmental sustainability.
Discover how digital signatures could benefit your business
What Industries and Use Cases Are There for Digital Signatures?
Digital signatures have widespread applications across various industries and use cases.
- Legal sector: signing contracts, agreements, and legal documents, ensuring authenticity and integrity.
- Banking and financial services: secure transactions, including loan approvals, investment agreements, and banking documents.
- Healthcare: consent forms, medical records, and prescriptions.
- Government and Public Sector: official documents, permits, and licenses.
- Real estate transactions: property sales contracts, rental agreements, management documents, consent forms.
- HR: employment contracts, appraisals, policies and handbooks, training and certification documents.
There are many other industries which benefit from the efficiency, security, and legal validity offered by digital signatures.
How to Choose the Right Document Signing Solution
When selecting the right digital signature solution, several factors should be considered. Firstly, assess the security measures in place, such as encryption and compliance with industry standards. Consider the integration capabilities with your existing software systems, such as document management or customer relationship management platforms. It’s also important to evaluate the scalability to ensure it aligns with your organization's needs. Additionally, you should also look for a solution that offers a user-friendly interface and supports a variety of document formats. Finally, consider the reputation, customer support, and track record of the provider to ensure a reliable and trusted partnership.
Discover GlobalSign’s Document Signing Solutions
Best Practices for Implementing Digital Signatures
Once you’ve assessed your organization's specific needs and goals, implementing digital signatures effectively requires implementing best practices.
- Develop policies and procedures around signature processes, and educate employees.
- Prioritize security by selecting a solution that employs robust encryption and authentication.
- To maximize efficiency, integrate the solution seamlessly into existing workflows .
- Regularly review and update your processes to stay compliant with relevant requirements and regulations.
- Provide adequate training and support to ensure smooth adoption and usage across the organization.
Once your IT administrator has taken the steps necessary to enable digital signatures for your organization, digitally signing a document is just as easy taking a pen to a piece of paper!
Future Trends in Digital Signing
The future of digital signing will naturally be driven by advancements in technology, changes to regulations and standards (as well as new ones), and developments of integrations with other digital solutions. But what’s important to consider is that these trends will contribute to increased security, widespread adoption, and enhanced efficiency in the realm of electronic transactions and document signing.
With advancements in technology always being made, there is the potential for innovative authentication methods such as biometrics and AI-driven verification. The use of these technologies will enhance the security and reliability of both electronic and digital signatures.
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are recognizing the importance of establishing clear guidelines and legal frameworks for electronic transactions. There is expected to be emergence of new regulations and standards, along with changes to existing laws, leading to the development of more comprehensive and globally recognized regulations to ensure the validity and enforceability of digital signatures across borders.
Integrations with other digital solutions will also push the envelope on signatory capabilities. Digital signatures are becoming an integral part of end-to-end digital workflows, allowing for a seamless transition from document creation to signing and archiving.
To Summarize: Digital Signatures are More Secure
Signing a document electronically is becoming part of our everyday lives and can enhance your organizational workflows, customer and staff experience whilst providing security and if required, non-repudiation. The bottom line is; a digital signature is more secure than an image of a signature applied electronically, and there are several benefits to implementing a document signing solution to your business. The solution will vary depending on your organization’s industry and use case.
If you want to unlock the power of digital signatures for your organization, then GlobalSign can help. Our document signing solutions are designed to offer options to suit your organization’s needs and secure documents and streamline workflows with digital signatures and seals to provide confidence, integrity and trust.
Work with our team of experts to find the right signing solution for your organization
Editor’s Note: This blog was originally published on July 11, 2023 but has since been updated to reflect industry changes and new insights.







